Below is the article summary. Integration of viral DNA into host DNA.
Replicate by converting normal host proteins into prion proteins.

. Separation of viral nucleic acid from the capsid. Viral diseases are extremely widespread infections caused by viruses a type of microorganism. 1 Virus binds receptors on cell membrane and enters cell.
Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and consist of a single- or double-stranded. Are the first line of. Viruses are very tiny germs.
Separation of viral nucleic acid from the capsid e. Separation of viral nucleic acid from the capsid. Separation of viral nucleic acid from the capsid.
Viruses are even smaller than bacteria and require living hosts such as people plants or animals to multiply. Differs because bacteriophages leave the capsid outside the cell while animal virus entry involves the entry of the whole nucleocapsid. Integration of viral DNA into the host genome b.
Addition of an envelope d. There are many types of viruses that cause a wide variety of viral diseases. Coronavirus disease 2019 COVID-19 the highly contagious viral illness caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SARS-CoV-2 has had a catastrophic effect on the worlds demographics resulting in more than 38 million deaths worldwide emerging as the most consequential global health crisis since the era of the influenza pandemic of 1918.
Well go over some of. There are several types of viral disease depending on the underlying virus. 2 Reverse transcriptase catalyzes formation of DNA complementary to viral RNA 3 New DNA strand serves as a template for complementary DNA strand 4 Double-stranded DNA is incorporated into host cells genome.
A key feature of all viral infections is The answer is. Key features in common. 5 Viral genes transcribed to RNA.
These include the following. Addition of a lipid membrane to the virus. A key feature of all viral infections is the.
The most common type of viral disease is the common cold which is caused by a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract nose and throat. Finally the progeny virions must escape the host cell so that they can infect other cells. Otherwise they cant survive.
Disintegration destruction of host DNA c. A key feature of all viral infections is separation of viral nucleic acid from the CAPSID An infection in which the virus in continually present int the body is referred to as. It is possible to vaccinate against many serious viral infections such as measles mumps hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Viruses are like hijackers. Addition of a lipid membrane to the virus. A key feature of all viral infections is the separation of viral nucleic acid from the capsid.
For the full article see virus. Disintegration of host DNA. Herpesviruses key features Large enveloped double stranded DNA virus Found in all vertebrates examined Narrow host range In mammals they likely coevolved during speciation Infection persists for life and is never cleared Establishes noncytopathic infection with limited viral gene expression and no virus production Latency.
They also cause severe illnesses such as HIVAIDS Ebola and COVID-19. By The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. A nucleic acid genome that is made of DNA or a RNA tucked inside of capsid.
A virus must first recognize and attach to a specific living cell prior to entering it. Separation of viral nucleic acid from the capsid. In the case of T-even phages the.
A viral disease is any condition thats caused by a virus. These viruses include chikungunya virus Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus Japanese encephalitis virus Rift Valley Fever virus West Nile virus Ross River virus Zika virus Zika Virus Infection Zika virus infection is a mosquito-borne viral infection that typically causes no symptoms but can cause fever rash joint pain or infection of the membrane that covers the. An aggressive worldwide vaccination campaign headed by the World Health Organization WHO managed to wipe out smallpox.
Viruses cause familiar infectious diseases such as the common cold flu and warts. Virus Microscopic simple infectious agent that can multiply only in living cells of animals plants or bacteria. When a virus enters your body it invades some of your cells and takes over the cell machinery redirecting it.
A protective protein shells or a capsid. Enzymes remove viral protein coat. After penetration the invading virus must copy its genome and manufacture its own proteins.
A key feature of all viral infections is the A. Disintegration of host DNA. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites.
Skin and mucous membranes are the first line of nonspecific defense b. Learn about the structure and features of viruses and the diseases caused by them. Immunisation against viral infection is not always possible.
An infection in which the virus is continually present in the body is referred to as. A key feature of all animal viral infections is the a. Integration of viral DNA into host DNA.
They are made of genetic material inside of a protein coating. A key feature of all viral infections is the.
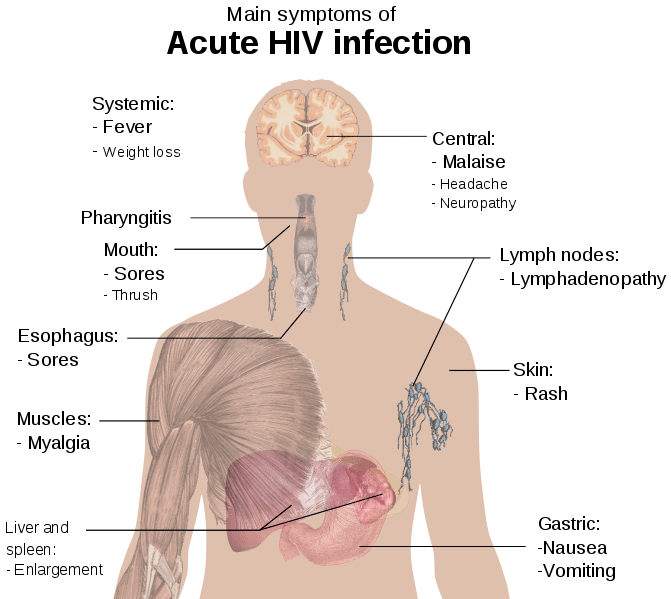
Viral Infection Viral Structure Viral Replication Teachmephysiology
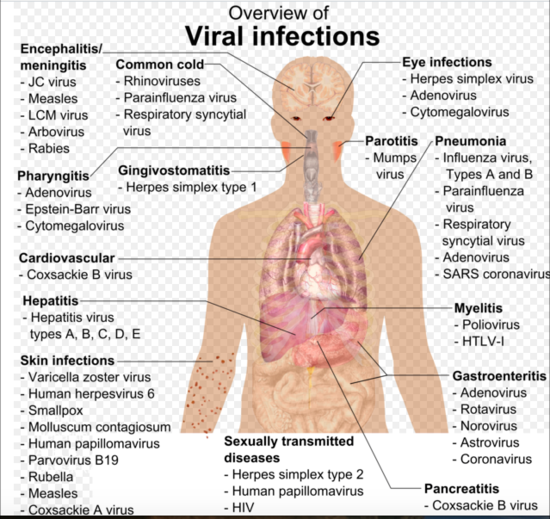
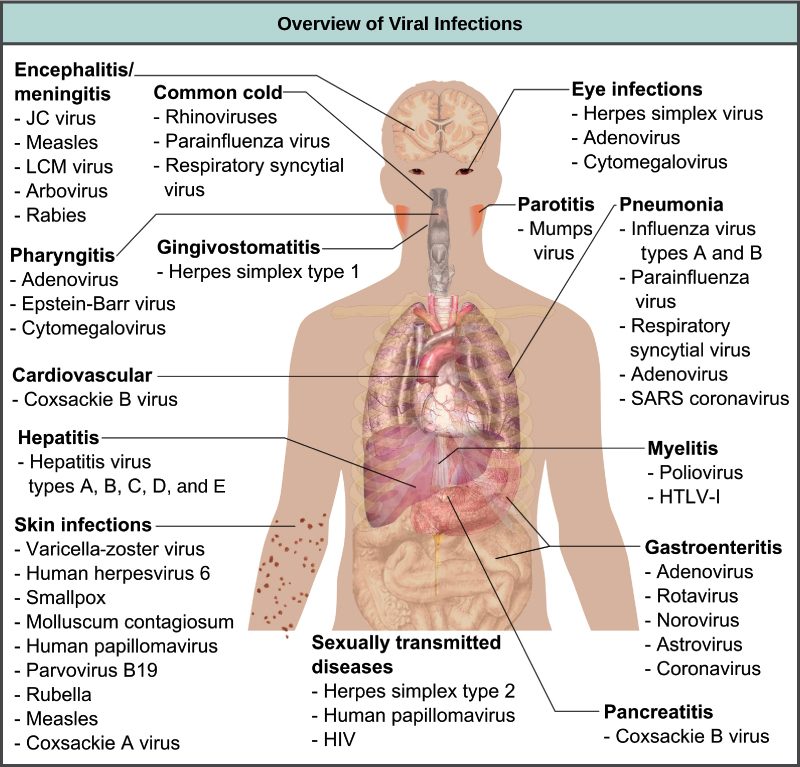
0 Comments